Appearance
造火箭从synchronized开始
About 2468 wordsAbout 8 min
2022-06-02
造火箭从synchronized开始
synchronized 原理和对象头
对象头长什么样子
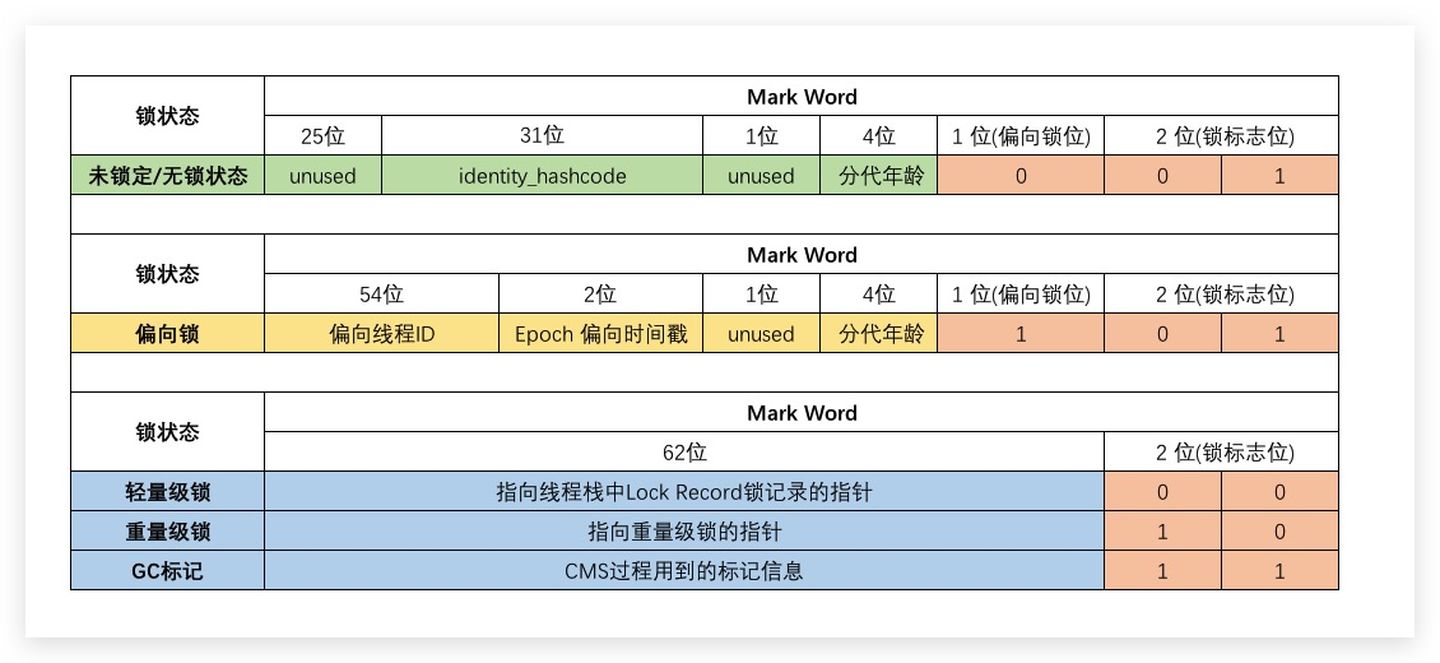
| 原生类型 | 内存大小(byte) | 原生类型 | 内存大小(byte) |
|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | 1 | byte | 1 |
| short | 2 | char | 2 |
| int | 4 | float | 4 |
| long | 8 | double | 8 |
concurrency.ObjectDemo object internals:
OFF SZ TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 8 (object header: mark) 0x0000000000000005 (biasable; age: 0)
8 4 (object header: class) 0xf800c105
12 4 int ObjectDemo.a 0
16 2 char ObjectDemo.b
18 6 (object alignment gap)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 6 bytes external = 6 bytes total代码如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jol</groupId>
<artifactId>jol-core</artifactId>
<version>0.16</version>
</dependency>public class ObjectDemo {
int a;
char b;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
ObjectDemo objectDemo = new ObjectDemo();
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(objectDemo).toPrintable());
}
}升级过程
- 一个对象默认是无锁或者可偏向无锁状态。
- 当被某个线程加锁后变为偏向锁状态。
- 多个线程无竞争交替获取锁,该锁升级为轻量级锁。
- 一个线程占有锁,其它线程尝试获取该锁,该锁升级为重量级锁。
抛出的问题
hashcode 是不是真的在对象头中
public class Example2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
System.out.println("初始状态");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
System.out.println("调用 hashcode 方法之后");
int hashCode = lock.hashCode();
// 将hashcode转二进制方便对比
System.out.println(Long.toBinaryString(hashCode));
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
}
}
public class ObjectUtils {
private static Unsafe UNSAFE;
static {
try {
Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafe.setAccessible(true);
UNSAFE = (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String getMarkWord(Object object) {
long mark = UNSAFE.getLong(object, 0L);
return CodeUtils.toBinary(mark);
}
}
public class CodeUtils {
static final String[] ZERO_RUNS;
static {
ZERO_RUNS = new String[16];
String s = "";
for (int c = 0; c < ZERO_RUNS.length; c++) {
ZERO_RUNS[c] = s;
s += "0";
}
}
public static String toHex(long x) {
String s = Long.toHexString(x);
int deficit = 16 - s.length();
return "0x" + ZERO_RUNS[deficit] + s;
}
public static String toStandardBinary(long x) {
String s = Long.toBinaryString(x);
int zero = 64 - s.length();
char[] data = new char[zero];
StringBuilder text = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
text.append("0");
}
s = text + s;
int i = 0;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
while (i < 64) {
builder.append(s, i, i += 8).append(" ");
}
return builder.toString();
}
public static String toBinary(long x) {
String s = Long.toBinaryString(x);
int zero = 64 - s.length();
char[] data = new char[zero];
StringBuilder text = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
text.append("0");
}
s = text + s;
int i = 0;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
while (i < 64) {
builder.append(s, i, i += 8).append(" ");
}
return builder.toString();
}
}运行结果如下:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
调用 hashcode 方法之后
10110111101100101011000010010
00000000 00000000 00000000 00010110 11110110 01010110 00010010 00000001可以看到hashcode是10110111101100101011000010010,把对象头中第26位到56位复制出来,去掉空格也是这个数字。
初始状态是什么?
public class Example1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
System.out.println("初始状态");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));;
}
}结果是00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 可以看到这是无锁状态。 因为j vm 偏向锁是延迟4s开启的,那把这个延迟设置为0之后呢? 在 VM 参数里加上-XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0,再次启动,发现结果变了,此时是 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000101这是一个偏向锁的状态。 所以结论是:锁的初始状态根据偏向锁是否开启和延迟相关,默认是无锁状态。
单线程加锁过后是什么样子?
首先看偏向锁延迟的情况
public class Example3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
System.out.println("初始状态");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
synchronized (lock){
System.out.println("加锁之后");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
}
System.out.println("锁释放之后");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
}
}00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
加锁之后
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001000 11001010 01001001 11100000
锁释放之后
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001刚开始是无锁状态,加锁之后变为轻量级锁,释放之后又变为无锁状态。除了锁状态位以外的位置,都是记录的线程栈中Lock Record锁记录的指针,即11 00001000 11001010 01001001 111000。
关闭偏向锁延迟看看。-XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0。
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000101
加锁之后
00000000 00000000 01111111 11000000 00111101 10000000 10001000 00000101
锁释放之后
00000000 00000000 01111111 11000000 00111101 10000000 10001000 00000101结果完全不一样了,刚开始的时候是无论什么时候都是偏向锁状态,只是在加锁和释放锁之后 mark word 中都记录了当前**偏向线程的id(前54位) **。 那这个id是不是真是当前偏向线程的id呢,得找办法看一下。修改代码并关闭偏向锁延迟
public class Example4 {
private static final String command = "jstack %s |grep main";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 打印 Thread Id
printThreadInfo();
Object lock = new Object();
System.out.println("初始状态");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 输入线程的16进制id
String tid = scanner.nextLine();
String s = Long.toBinaryString(Long.valueOf(tid, 16));
System.out.println("从jstack中获取的线程id:");
System.out.println(s);
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("加锁之后");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
}
System.out.println("锁释放之后");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
}
private static void printThreadInfo() throws IOException {
String name = ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getName();
System.out.println(name);
String pid = name.split("@")[0];
System.out.println("Pid is:" + pid);
ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new ProcessBuilder();
processBuilder.command("bash", "-c",String.format(command, pid));
Process process = processBuilder.start();
InputStream inputStream = process.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, os);
System.out.println(new String(os.toByteArray(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}运行代码,然后从jps获取当前进程的pid,然后执行命令jstack ${pid}|grep main获取到主线程的16进制id,输入然后回车。
Pid is:24248
"main" #1 prio=5 os_prio=31 tid=0x00007fe55580c800 nid=0x2503 runnable [0x000000030dbd0000]
at concurrency.Example4.main(Example4.java:20)
初始状态
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000101
00007fe55580c800
从jstack中获取的线程id:
11111111110010101010101100000001100100000000000
加锁之后
00000000 00000000 01111111 11100101 01010101 10000000 11001000 00000101
锁释放之后
00000000 00000000 01111111 11100101 01010101 10000000 11001000 00000101经过比较,线程id完全一致。
交替获取锁升级轻量级锁
public class Example5 {
static final Object LOCK = new Object();
static final int COUNT = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0
System.out.println("加锁前");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(LOCK));
TestThread t1 = new TestThread("t1");
TestThread t2 = new TestThread("t2");
t1.other = t2;
t2.other = t1;
t1.start();
}
static class TestThread extends Thread {
Thread other;
public TestThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; i++) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
System.out.println("线程" + getName() + "获取到锁了");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(LOCK));
}
if (!other.isAlive()) {
other.start();
} else {
LockSupport.unpark(other);
}
LockSupport.park();
}
}
}
}加锁前
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000101
线程t1获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 01111111 11101100 00011100 10010010 01011000 00000101
线程t2获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00100110 01111010 10010000
线程t1获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00010110 01001010 10010000
线程t2获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00100110 01111010 10010000
线程t1获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00010110 01001010 10010000
线程t2获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00100110 01111010 10010000
线程t1获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00010110 01001010 10010000
线程t2获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00100110 01111010 10010000
线程t1获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00010110 01001010 10010000
线程t2获取到锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 00001111 00100110 01111010 10010000加锁前是偏向锁,t1获取到锁后锁偏向t1,然后t2又获取到锁了,此时升级为轻量级锁,t1和t2交替获取锁,期间没有发生竞争,锁一直是轻量级锁。
线程竞争真的会升级为重量级锁吗
public class Example6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0
Object lock = new Object();
System.out.println("加锁前");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
System.out.println("加锁后");
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("t1 来抢锁了");
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("t1 加锁了--------");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
}
});
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("main 加锁了--------");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
t1.start();
// 让 t1 有时间来竞争锁
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
Thread.sleep(200);
}
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("两个线程都释放锁了");
System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getMarkWord(lock));
}
}加锁前
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000101
加锁后
main 加锁了--------
00000000 00000000 01111111 11001011 11001011 00000000 10001000 00000101
t1 来抢锁了
00000000 00000000 01111111 11001011 11001011 00000001 10110011 00111010
t1 加锁了--------
00000000 00000000 01111111 11001011 11001011 00000001 10110011 00111010
两个线程都释放锁了
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001初始状态还是可偏向状态的锁,main 加锁后变为偏向锁,t1 来竞争的时候main还未释放锁,此时锁升级为重量级锁,t1拿到锁之后还是重量级锁(指向同一个监视器),当所有线程都释放锁之后,锁降级为无锁状态。
ObjectMonitor 监视器
ObjectMonitor 包含 _WaitSet、_EntryList、_cxq、_owner 和 _recursions。
- WaitSet。存放 waiting 状态的线程,线程调用 lock.wait() 后会进入这里。
- EntryList。调用 synchroized 后会进入这里,获取锁失败后进入 cxq。
- cxq。获取锁失败的线程会进入这里,从头部插入。
- _owner。存放当前拥有锁的线程。
- _recursions。重入次数。
AQS 队列是 FIFO,那 synchronized 的队列呢?
public class SynchronizedExample {
static List<Thread> list = new ArrayList<>();
static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--thread executed");
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t" + i);
list.add(t);
}
synchronized (lock) {
for (Thread thread : list) {
System.out.println(thread.getName() + "-启动顺序--正序0-9");
// 此时主线程没有释放锁,线程0-9将会在 EntryList 中
thread.start();
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println("-------执行顺序--正序9-0");
}
}
}结果如下:
t0-启动
t1-启动
t2-启动
t3-启动
t4-启动
t5-启动
t6-启动
t7-启动
t8-启动
t9-启动
-------执行顺序--正序9-0
t9--thread executed
t8--thread executed
t7--thread executed
t6--thread executed
t5--thread executed
t4--thread executed
t3--thread executed
t2--thread executed
t1--thread executed
t0--thread executed超出认知的 notify 和 notifyAll
public class Example8 {
static final List<Thread> LIST = new ArrayList<>();
static final List<String> EXECUTED = new ArrayList<>();
static final Object LOCK = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
// 因为启动有间隔时间,所以这10个线程不存在竞争,所有的线程都在 waitSet 中
synchronized (LOCK) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--等待被唤醒");
// 此时在 cxq 中
LOCK.wait();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "醒了----");
EXECUTED.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
// LOCK.notify();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "S" + i).start();
Thread.sleep(10);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
LIST.add(new Thread(() -> {
//11111
synchronized (LOCK) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--thread executed");
try {
EXECUTED.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t" + i));
}
synchronized (LOCK) {
for (Thread thread : LIST) {
System.out.println(thread.getName() + "-启动");
// 此时主线程没有释放锁,线程1-5加锁失败后会进入 cxq 中, head 5 4 3 2 1
thread.start();
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println("-------执行顺序--正序5-0");
// 此时WaitSet 中的线程会移动到 cxq 的头部
LOCK.notifyAll();
// LOCK.notify();
}
// 此时主线程释放锁,依次从 EntryList
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(EXECUTED);
}
}t0--thread executed
t1-启动
t2-启动
t3-启动
t4-启动
t5-启动
-------执行顺序--正序5-0
t0醒了----
t5--thread executed
t4--thread executed
t3--thread executed
t2--thread executed
t1--thread executed